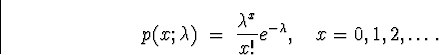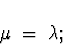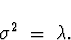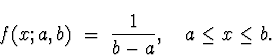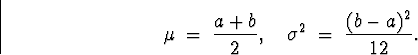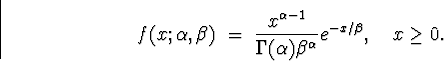

Next: .
The exam is closed book. You will be provided with tables and
formulas. You may use calculators.
Formulas and Tables.
In all cases below, we show the values where the p.m.f. or
p.d.f. is positive.
Discrete Probability Distributions.
- 1.
- Binomial
- A.
- Parameters:
n = number of trials;
p = probability of success on each trial.
It is required that n is a positive integer, and p is between
and 1.
- B.
- Probability Mass function:
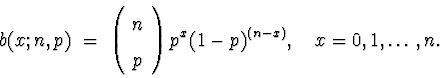
NOTE: the binomial coefficient should have x in place of p -- sorry about
the error.
- C.
- Mean and Variance:
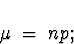

- 2.
- Poisson
- A.
- Parameters:
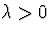 .
. - B.
- Probability Mass function:
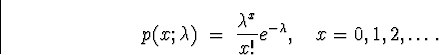
- C.
- Mean and Variance:
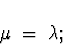
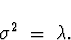
Continuous Probability Distributions.
- 1.
- The Uniform distribution.
- A.
- Parameters: a < b.
- B.
- Probability Density Function:
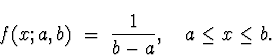
- C.
- Mean and Variance:
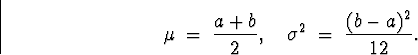
- 2.
- The Exponential Distribution.
- A.
- Parameters:
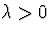 .
. - B.
- Probability Density Function:
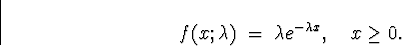
- C.
- Mean and Variance:
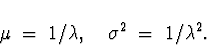
- 3.
- The Gamma Distribution.
- A.
- Parameters:
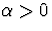 and
and 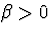 .
. - B.
- Probability Density Function:
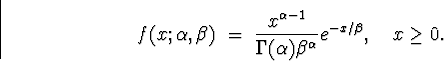
- C.
- Mean and Variance:
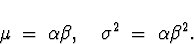
SOLUTIONS to the study guide questions
Dennis Cox
3/8/2001
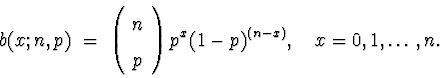
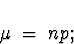

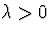 .
.