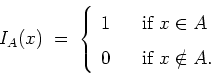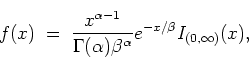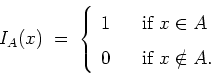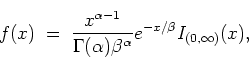Next: Solution to Exercise 1.
Solutions to Final Exam
STAT 431/531
Dennis D. Cox
Notations; some useful distributions:
- +
- Indicator functions:
- +
- uniform(a,b) has pdf
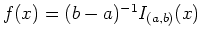 ,
,
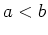 .
.
- +
- exponential(
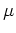 ) has pdf
) has pdf
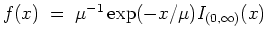 ,
,
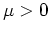 .
.
- +
- Poisson(
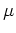 ) has pmf
) has pmf
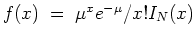 where
where
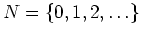 is the set of nonnegative integers
(natural numbers),
is the set of nonnegative integers
(natural numbers), 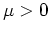 .
.
- +
- The binomial distribution
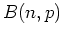 has pmf
has pmf
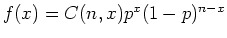 where
where
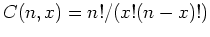 if
if
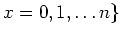 and
and 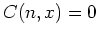 otherwise. Here,
otherwise. Here,
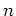 is a positive integer and
is a positive integer and 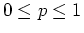 .
.
- +
- Bernoulli(p) is B(1,p).
- +
- The Gamma function satisfies
- +
- The gamma(
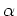 ,
,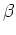 ) distribution has pdf
) distribution has pdf
for 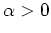 and
and 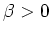 .
.
- +
- The
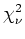 distribution is the same as the
gamma(
distribution is the same as the
gamma(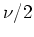 ,
, 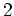 ) distribution.
) distribution.
Dennis Cox
2003-01-18